
Blog
True love for great sound unites us.
Blog
True love for great sound unites us.
72% of all desktop computers run Windows software. Windows is great for many applications, office tasks, gaming, and other everyday activities. Unfortunately, it is not optimized for audio use.
Unlike specialized operating systems such as macOS or Linux, Windows isn't built from the core for real-time audio processing. This means that the Windows task scheduling mechanism, designed primarily for general computing tasks, doesn't prioritize real-time audio processing. As a result, audio-related tasks can face delays or interruptions from other system processes, resulting in audio dropouts and audio glitches, especially when using demanding applications like DAWs.
While using Windows for audio production, you may encounter challenges in achieving consistent and reliable audio performance. If you're using a USB audio interface and notice such problems, we suggest following the steps provided below to help mitigate this.
Before blaming your operating system, it's essential to explore other potential causes of audio problems. We've compiled a checklist to help you troubleshoot common audio issues effectively.
If all the above points comply, it is likely the reason for your trouble lies within the Windows operating system. Please try the following steps to improve the behavior:
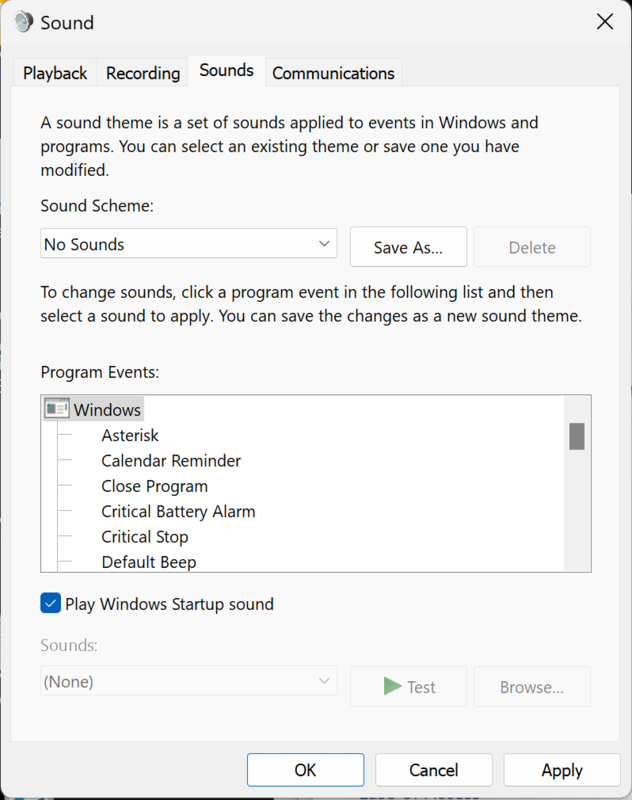
Search for "Control Panel" -> "Hardware and Sound" -> "Sound" -> "Sounds" tab -> "Sound Scheme menu" -> choose "No Sounds" -> "OK"
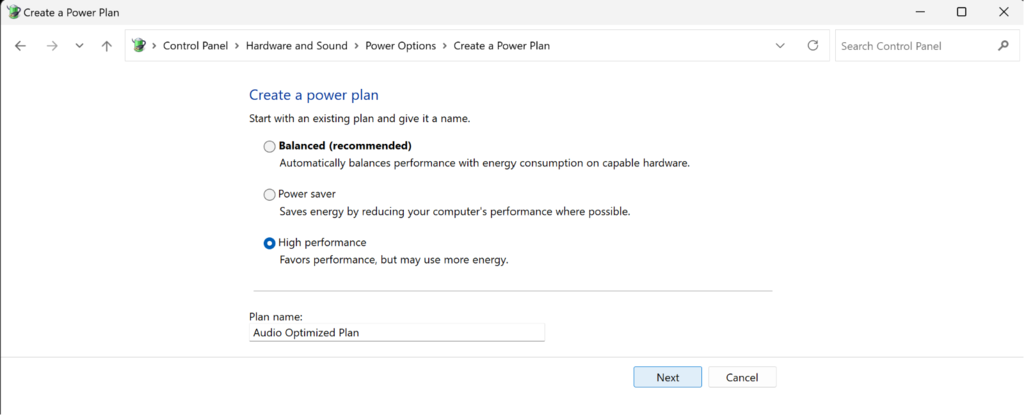
Search for "Power Options" -> "Create a power plan" -> "High Performance" -> Name your plan, for example, "Audio Optimized Plan" -> Set "Turn off the display" and "Put the computer to sleep" to "Never" -> "Create"
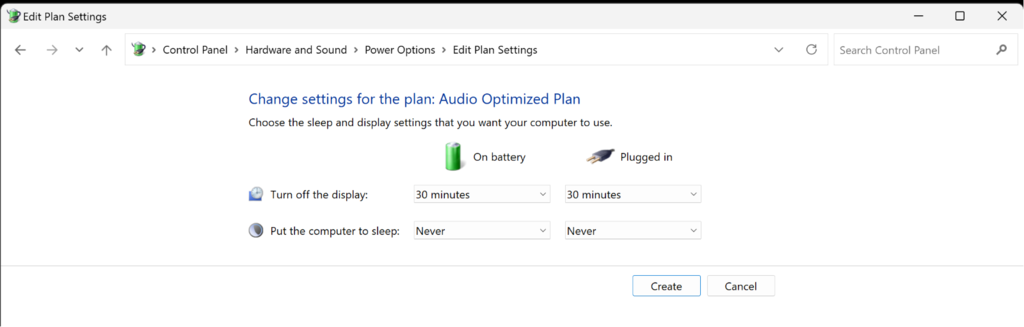
Search for “Edit power plan” -> “Change advanced power settings” -> “USB settings” -> On battery / Plugged in “disable” -> “OK”
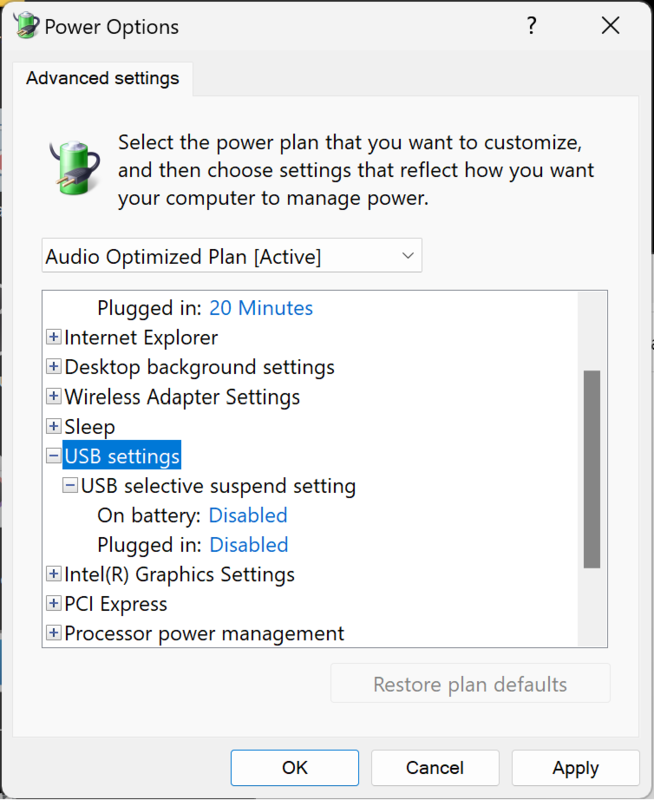
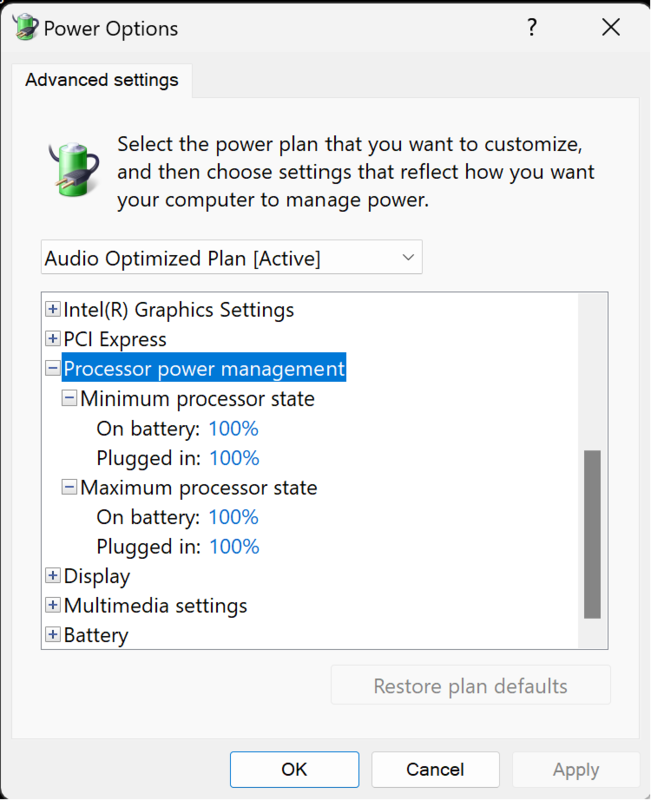
Select "Change Plan Settings" for your custom power plan -> Open "Advanced power settings" -> Expand "USB settings" -> Disable "USB Selective suspend" -> Expand "Processor power management" -> Set the minimum and maximum process state to 100.
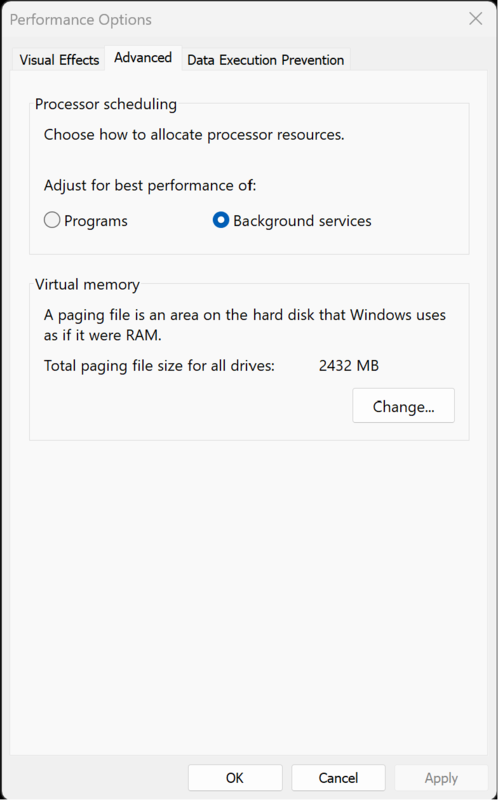
Search for "Advanced system settings" -> "Advanced" tab -> "Performance” -> “Settings…" -> "Advanced" tab -> activate "Background services" -> "Apply" -> “OK”
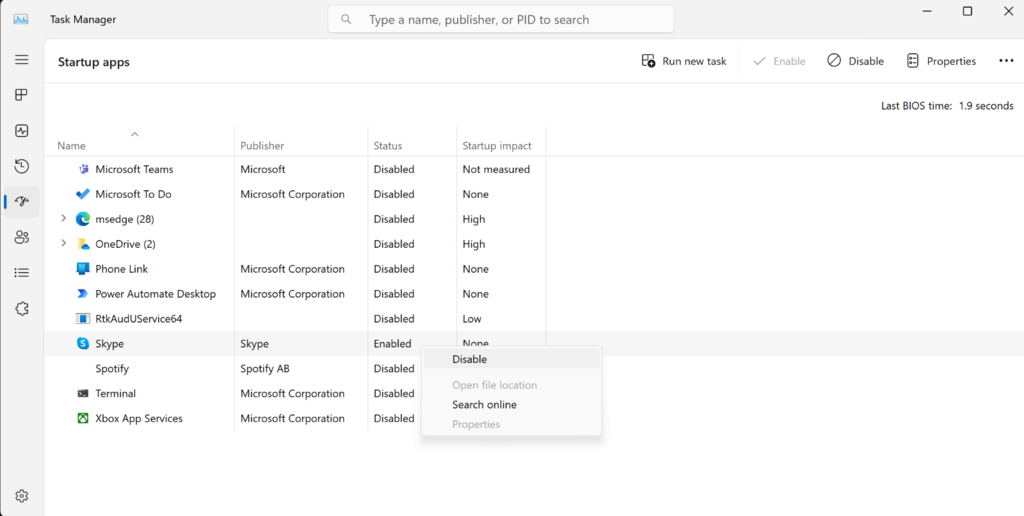
Search for "Task Manager" -> "More details" -> "Startup" tab -> select all apps that are not required for automatic launch -> "Disable"
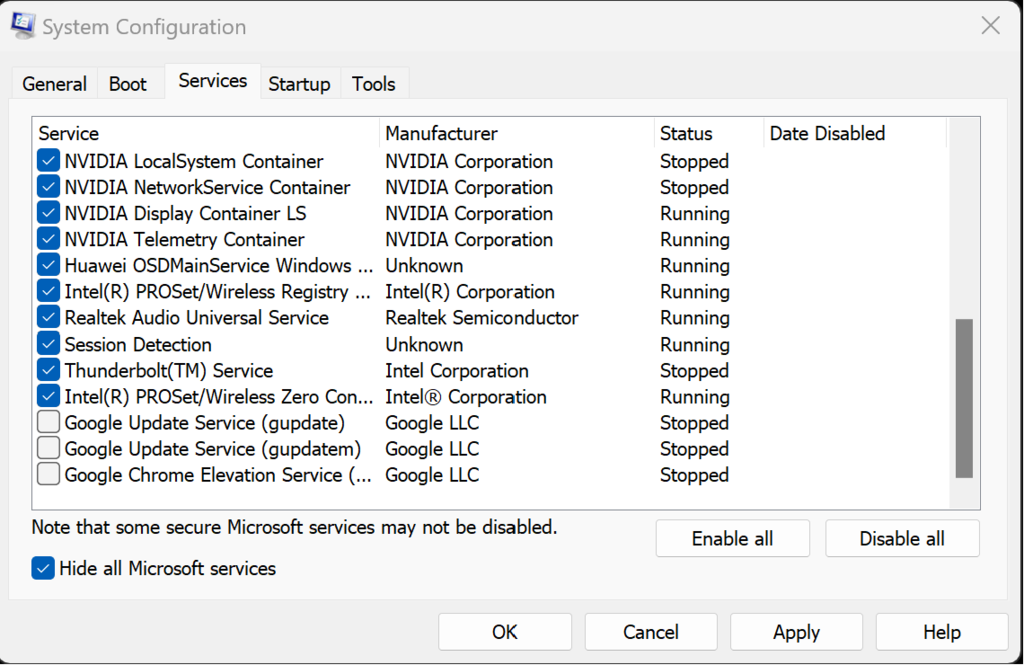
Search for "System Configuration" -> "Services" tab -> check "Hide all Microsoft services" -> Remove check from all applications you don't need -> "Apply" -> "OK" -> "Restart" popup
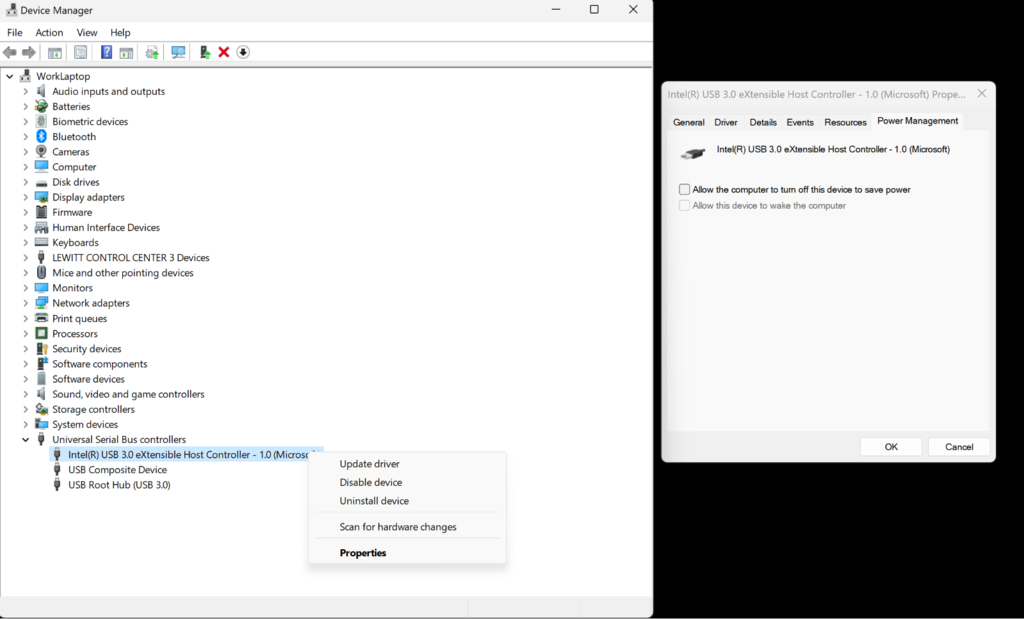
Search for "Device Manager" -> open dropdown menu of “Universal Serial Bus controllers” -> right-click all items -> "Properties" -> "Power Management" tab -> uncheck "Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power" -> “OK”
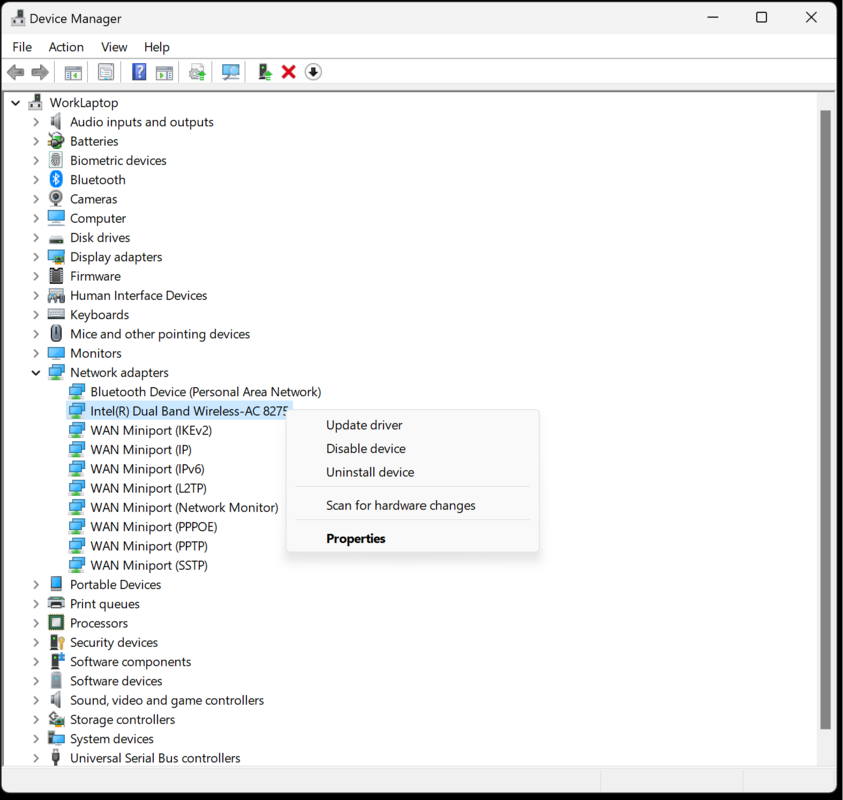
Sometimes network cards cause audio issues, if the network card is not the cause of an issue it is advised to revert this action. Search for "Device Manager" -> open dropdown menu of “Network adapters” -> right-click items -> “disable”
To conserve energy, some CPUs have low-power modes called "C-states" or "C-modes" implemented. Disabling C-states in your computer's BIOS might resolve audio issues.
This process varies depending on your PC's hardware, and we strongly advise getting in touch with the motherboard manufacturer for assistance.
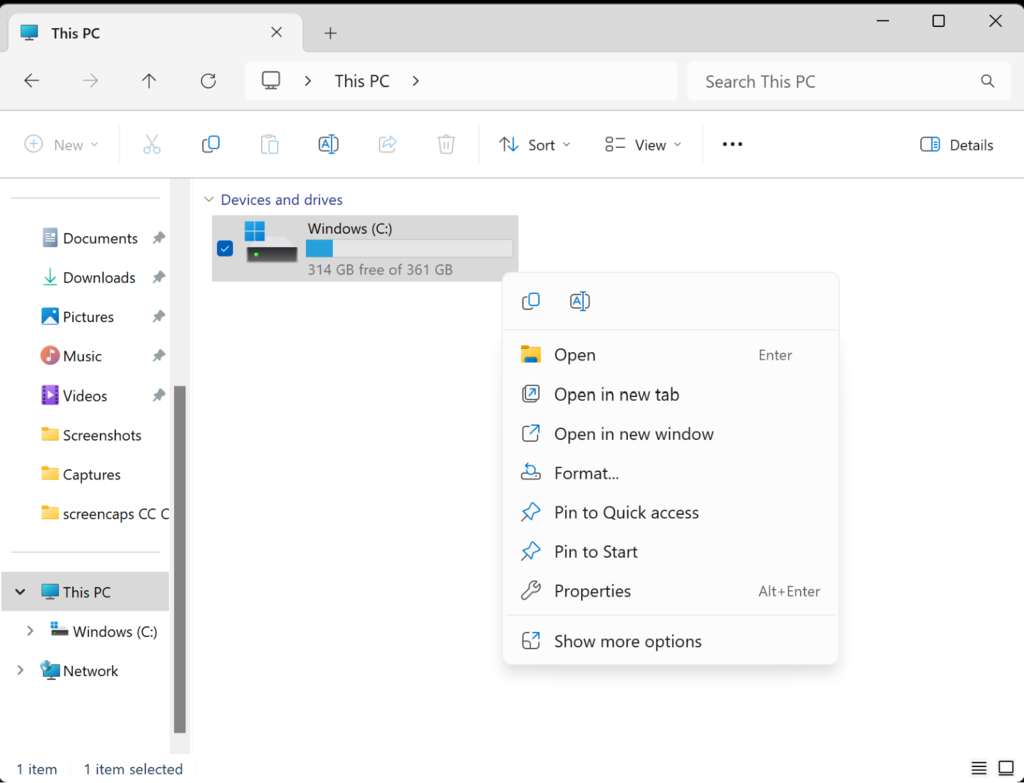
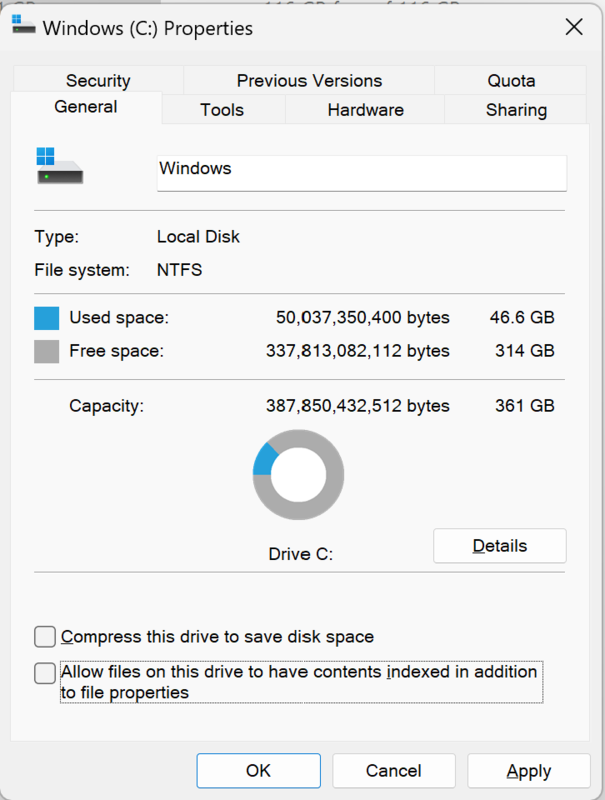
Locate your hard drive(s) intended to use for audio work -> Right-click "Properties" -> "General" tab -> uncheck both "Compress this drive to save disk space" and "Allow files on this drive to have contents indexed" -> "Apply" -> "OK"
We really hope the information we shared has helped you to sort out any Windows and Audio problems you've had. If things are still not working right, don't hesitate to get in touch through our customer support.